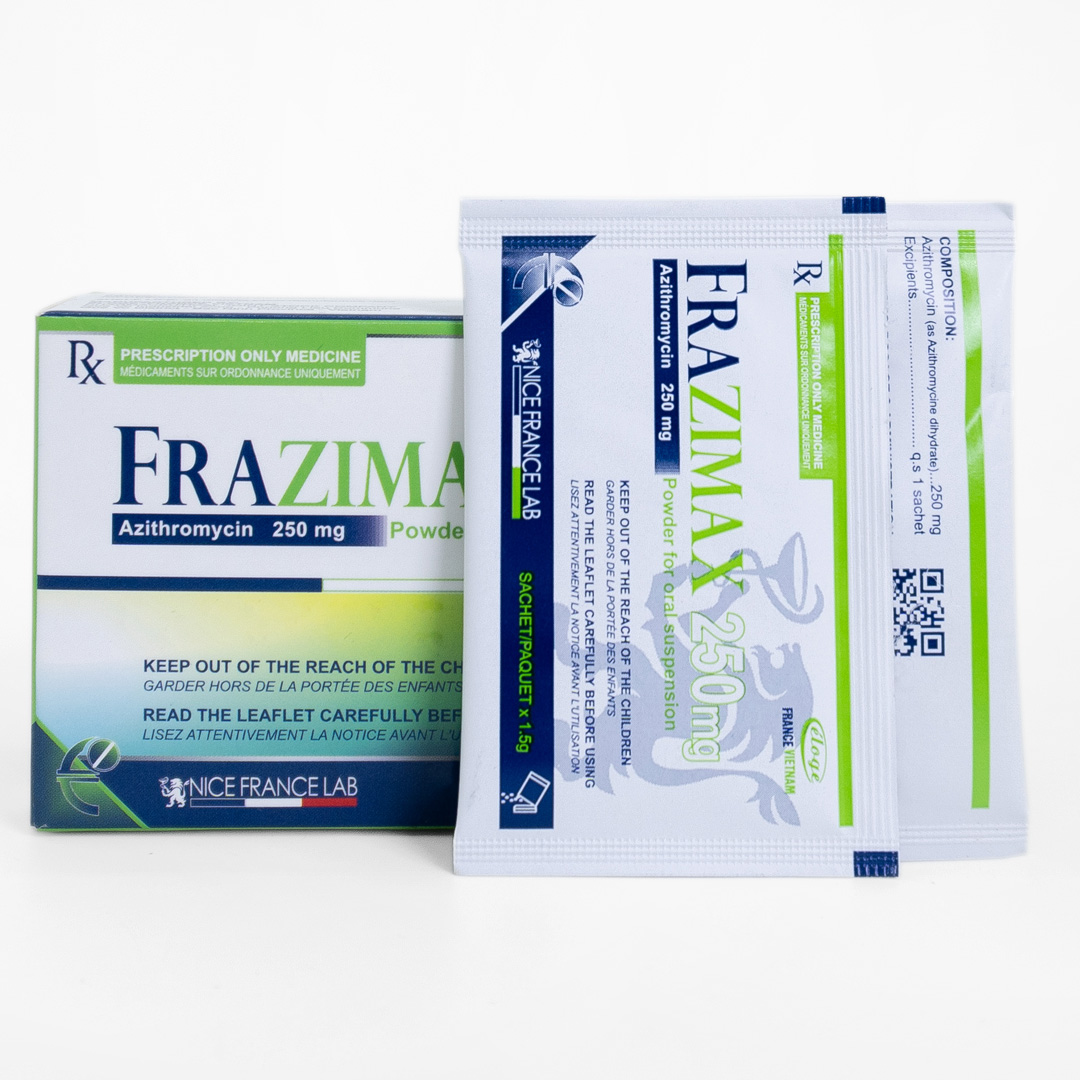
FORMULA:
Azithromycine: 250 mg
Sucrose, Aerosil, Aspartam, strawberry-flavored powder q.s for 1 sachet.
INDICATIONS:
Frazimax oral powdered medicine is indicated to treat infections:
Upper respiratory tract: ear, nose, throat such as sinusitis, pharyngitis, otitis, tonsillitis
Lower respiratory tract: acute bronchitis, pneumonia
Skin and soft tissue: pimples, purulent skin disease, impetigo due to Staphylococcus aureus
Uncomplicated sexually-transmitted diseases such as urethritis and cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis or non-MDR Neisseria gonorrhoeae
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Not for patients with hypersensitivity to azithromycine or any antibiotic in the macrolid group.
ADVERSE DRUG REACTION (ADR):
Azithromycine is an easily-absorbed medicine, with low rate of ADR. Most ADRs are light or mild, and can disappear when the treatment is halted.
Most common is digestive disorder with symptoms such as nausea, stomachache, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Less common are fatigue, headache, dizziness, rash, itchiness.
Rare are angioedema, rising transaminase enzyme, temporary light reduction of neutrophil.
Inform your doctor of ADR encountered when using the medicine.
TREATMENT OF ADR:
If there are serious ADR, stop using Azithromycine.
DOSAGE AND USAGE:
Recommended doses as:
Adult:
For treatment of STDs such as urethritis, cervicitis due to Chlamydia trachomatis infection, take a single 1g dose.
Other indications (bronchitis, pneumonia, pharyngitis, skin and soft tissues infections): first day takes a 500 mg dose, then use a single dose of 250 mg/day for 4 days.
Elderly:
Same dose as adult.
Children above 6 months old:
On the first day, take 10 mg/kg body weight, then 5 mg/kg every day, from the 2nd to the 5th day, take 1 dose each day.
Usage:
Frazimax is taken orally, so take at least 1 hour before meals or 2 hours after meals. Mix the medicine with warm water and take immediately.
This medicine is only to be used according to the doctor’s instructions.
INTERACTIONS:
Food slows the absorption of Azithromycine, so take the medicine far away from meals.
Azithromycine is only used at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after taking antacids.
Do not use concurrently Azithromycine and ergot derivatives (e.g., ergotamine, dihydroergotamin) because of poisoning risk.
Azithromycine can affect digoxin metabolism in the intestine, and there is a probability of the level of digoxin increasing, so the digoxin level should be monitored when used concurrently.
When used Azithromycine with warfarin, the coagulation time of the patient should be monitored.
KEEP OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN