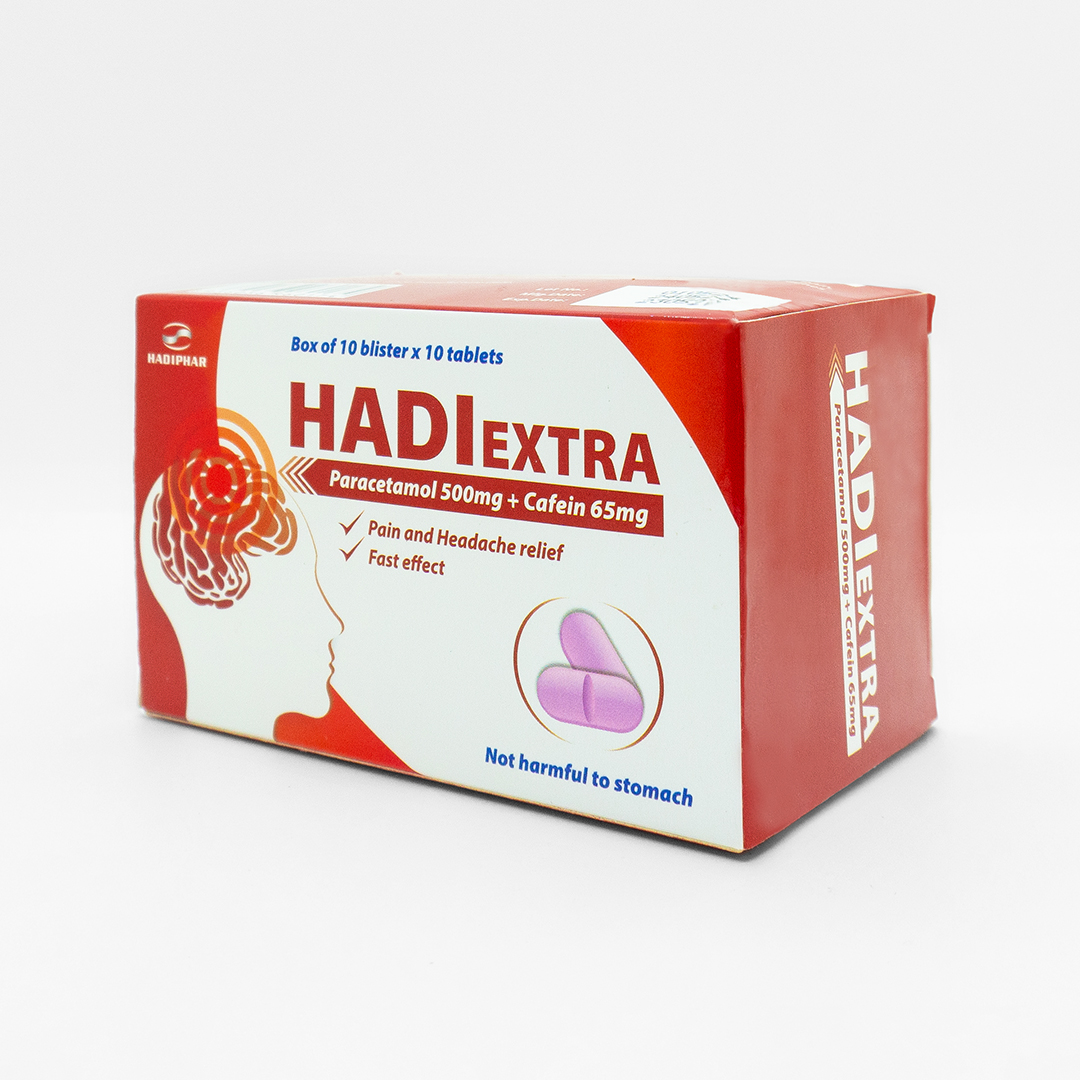
INDICATION: Quickly relieve aches and pains: headache, migraine headache, toothache, period pain, tendon and muscle aches, traumatic injuries pains, arthritis pains, sinusitis pains, aches and pains for cold and flu…
Relieve fever due to different causes.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
– Adults and children 16 years old and older: 2 caplets each 4-6 hours x 4 times daily.
Do not exceed 8 caplets in 24 hours.
Children from 12 to 15 years old: 1 caplet each 4-6 hours x 4 times daily. Do not exceed 4 caplets in 24 hours.
– Not recommended for children under 12 years old
Usage: Taken oraly
CONTRAINDICTION:
Patient hypersensitive to any ingredient of drug.
Patient of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Patient of severe liver failure, tachycardia, ventricular beats.
CAUTION:
Caution with use in patient of anemia.
Avoid using alcohol beverage when using drug.
PREGNANT AND BREAST-FEEDING WOMAN:
Pregnant and breast feeding women are not recommend to use drug. Consult doctors carefully before use.
EFFECT ON DRIVING AND MACHINE OPERATION
This drug does not cause drowsiness so it can be used for who have to drive or operate machine.
DRUG INTERACTION:
High-dose and long use of paracetamol can increase slightly the anticoagulant effect of coumarin and indandion derivatives.
Caution about the severe fever-relieving effect in patient using drug with phenothi-azine and other heat-reducing therapy.
Overuse of alcohol in long time can increase the harmful effect of paracetamol to liver. Decrease the effect of neural inhibitors (due to caffeine).
ADVERSE DRUG REACTION (ADR):
Drug allergy is rarely seen, sometimes skin rash or hives, but sometimes the symptoms can be more severe, going with fever or mucosa damage. In some unpopular cases, paracetamol causes the decrease of neutrophil, platelet and blood cell.
Caffeine can cause insomnia, jitter, and excitement.
Notice: Inform your doctor unexpected drug reaction in using drug.
OVERDOSE AND TREATMENT
For Paracetamol:
- Symptom:
Paracetamol toxicity can be caused by a single toxic dose, by repeated large doses of paracetamol (eg, 7.5-10 g daily, for 1-2 days), or by long-term use. Dose-dependent hepatic necrosis is the most serious acute toxic effect of overdose and can be fatal
Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain usually occur within 2 to 3 hours of taking a toxic dose. Methemoglobin blood, leading to cyanosis of the skin, mucous membranes and nails is a characteristic sign of acute poisoning with p-aminophenol derivatives; Small amounts of sulfhemoglobin may also be produced. Children tend to make methemoglobin more easily than adults after taking paracetamol.
In severe poisoning, there may be initial CNS stimulation, agitation and delirium. This may be followed by central nervous system depression; stupor, hypothermia; exhaust- ed; rapid, shallow breathing; fast, weak, irregular pulse; low blood pressure; and circulatory failure. Vascular collapse due to relative hypoxia and because of the central inhibitory effect, this effect occurs only with very large doses. Shock can occur if multiple vasodilation. Fatal choking convulsions may occur. Usually coma occurs before sudden death or several days after coma.
Clinical signs of liver damage become apparent within 2 to 4 days after ingestion of a toxic dose. Plasma aminotransferases are elevated (sometimes very high) and plasma bilirubin levels may also be elevated; Furthermore, when the liver is severely damaged, the prothrombin time is prolonged. It is possible that 10% of patients with untreated poisoning have severe liver damage; of which 10% to 20% eventually die of liver failure. Acute renal failure also occurs in some patients. Liver biopsy showed central lobular necrosis with the exception of the periportal region. In non-fatal cases, liver damage can be reversible in weeks or months.
* To solve:
Early diagnosis is important in the treatment of paracetamol overdose. There are methods for the rapid determination of drug plasma concentrations. However, treatment should not be delayed pending test results if the history suggests a serious overdose. When intoxication is severe, it is important to provide active supportive treatment. Gastric lavage in all cases, preferably within 4 hours of ingestion.
The primary detoxification therapy is the administration of sulfhydryl compounds, which presumably work in part by replenishing the liver’s stores of glutathione.
N-acetylcysteine is effective when taken orally or intravenously. The medicine must be given immediately if it has not been 36 hours since paracetamol has been taken. Treatment with N-acetylcysteine is more effective when the drug is administered less than 10 hours after taking paracetamol. When giving orally, dilute the N-acetylcysteine solution with water or a non-alcoholic beverage to get a 5% solution and must be drunk within 1 hour after mixing. Give oral N-acetylcysteine with a first dose of 140 mg / kg, then give another 17 doses, each dose of 70mg/kg every 4 hours. Discontinue treatment if plasma paracetamol test indicates a low risk of hepatotoxicity.
Adverse effects of N-acetylcysteine include skin rash (including urticaria, which does not require discontinuation), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and anaphylactic reactions.
If N-acetylcysteine is not available, methionine can be used. Alternatively, activated charcoal and/or salt bleach can be used, which may reduce paracetamol absorption.
For Caffeine:
*Symptom:
Caffeine overdose can lead to epigastric pain, vomiting, edema, tachycardia or arrhythmias, central nervous system stimulation (insomnia, restlessness, euphoria, agitation, tremor, tremor and convulsions).
It should be noted that for clinically significant caffeine overdose to occur with this product, the amount used will be related to the severe toxicity of paracetamol.
*To solve
Patients should receive general supportive care (eg, hydration and maintenance of vital signs). The use of activated charcoal may be beneficial when taken within an hour of an overdose, but can be considered up to four hours after an overdose. The CNS effects of overdose can be treated with intravenous sedation.
Sodium Bicarbonate:
High doses of sodium bicarbonate can cause stomach symptoms including belching and nausea. In addition, high doses of sodium bicarbonate can cause hyperkalemia; Electrolytes should be applied and the patient monitored..
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN
READ INSERTED LEAFLET CAREFULLY BEFORE USE
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR FOR MORE INFORMATION.
MANUFACTURED BY:
HA TINH PHARMACEUTICAL JOINT STOCK COMPANY
No.167 Ha Huy Tap Street, Nam Ha Ward, Ha Tinh City, Ha Tinh Province, Vietnam.