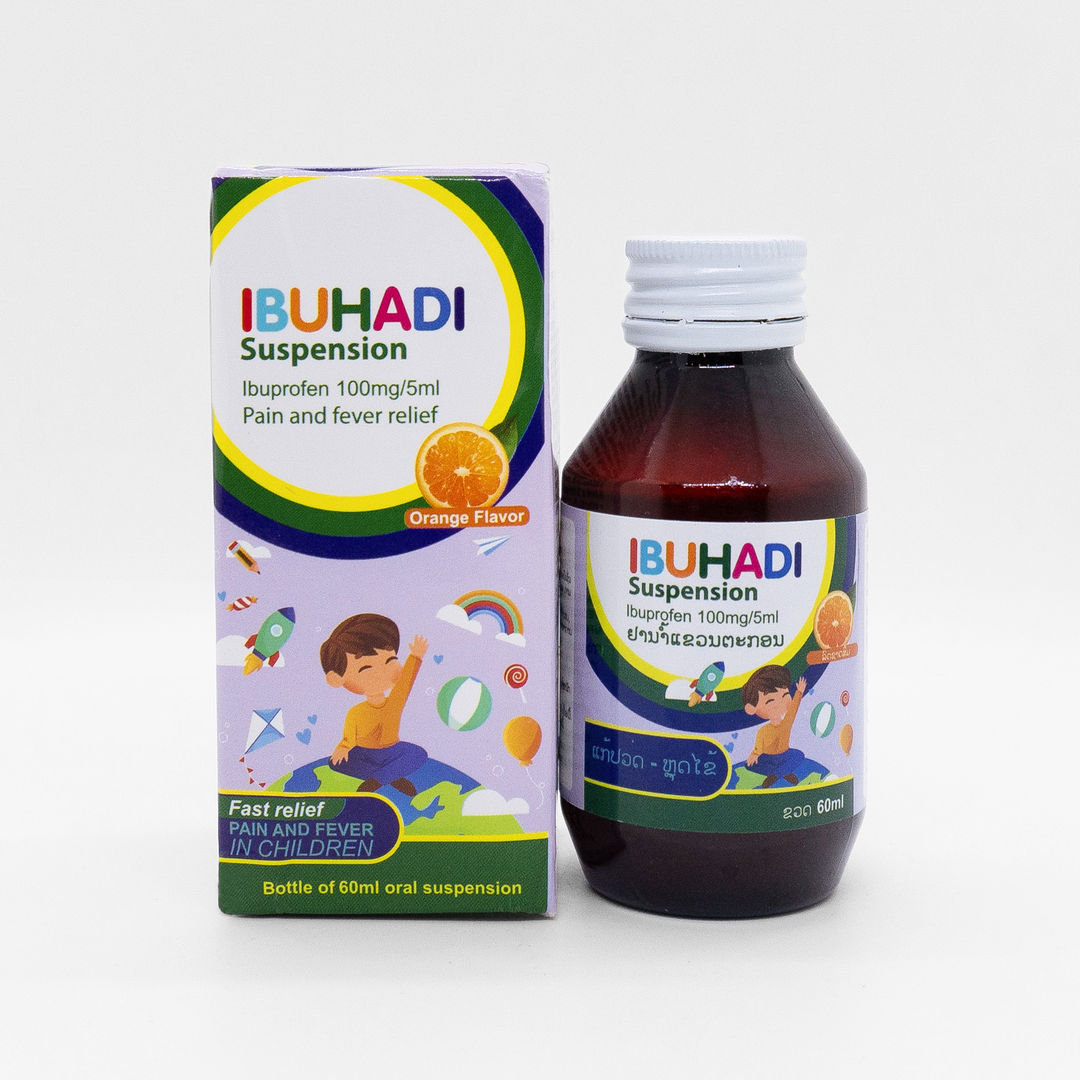
INDICATION:
Relieve mild to moderate pain in some cases such as dysmenorrhea, headache, toothache, pain and inflammation of tissue trauma. Relief of pain and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile
rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, joint pain from inflammation of the musculoskeletal system. Reducing fever in children.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION:
Dosage
Treatment of Pain and Fever
Children weighing < 5 kg or under 3 months old: Not recommended.
Children weighing ≥ 5 kg or more: 20 mg/kg body weight/day, divided into 3 times a day.
Children weighing ≥ 6 kg or more: 20 mg/kg body weight/day, divided into 3 times a day.
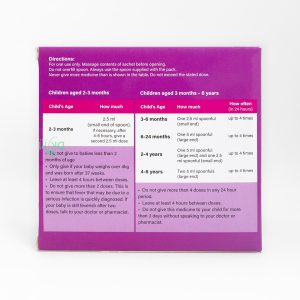
Newborns (6-12 months): Dose: 2.5 ml/time (measured with the measuring cup) 3-4 times/day.
Children (1-3 years old): Dose: 5 ml/time (measured with the measuring cup attached) 3 times/day.
Children (4-6 years old): Dose: 7.5 ml/time (measured with the measuring cup attached) 3 times/day.
Children (7-9 years old): Dose: 10 ml/time (measured with the measuring cup attached) 3 times/day.
Administration:
The interval between doses should be about 6-8 hours (or at least 4 hours).
Warnings:
Not for use in children under 3 months or weighing < 5 kg.
For children over 6 months: If symptoms persist for more than 3 days, consult a doctor.
For infants under 6 months: If symptoms persist for more than 24 hours, consult a doctor.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Hypersensitivity to Ibuprofen or any of the ingredients.
Peptic ulcer disease progression.
History of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation related to previous NSAID use.
Asthma, urticaria, angioedema, rhinitis associated with NSAID use.
Patients taking aspirin or other NSAIDs.
Patients with:
Bleeding disorders
Cardiovascular disease
Peptic ulcer disease
Kidney failure (glomerular filtration rate < 30 ml/min)
Children under 6 months
Pregnant women in the last three months
PRECAUTIONS & WARNINGS:
Care should be taken when administering Ibuprofen to the elderly.
May cause visual disturbances such as blurred vision.
Long-term use may impair kidney function and worsen kidney failure.
Use caution in patients with:
Hypertension, heart failure, or fluid retention.
History of gastrointestinal disease (ulcers, Crohn’s disease, colitis).
High doses (2400 mg daily) may increase the risk of stroke.
SIDE EFFECTS:
5-15% of patients may experience gastrointestinal side effects.
Common (ADR > 1/100):
Fatigue, fever
Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting
Headache, dizziness, restlessness
Hypersensitivity rash
Uncommon (ADR 1/1000):
Bronchospasm in asthma patients
Rhinitis, urticaria
Gastrointestinal bleeding, gastric ulcer
Drowsiness, insomnia, tinnitus
Adverse Effects:
Eyes: Visual disturbances
Ears: Hearing loss
Blood: Prolonged bleeding time
Rare (ADR < 1/1000):
Body: Edema, rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, alopecia
Central nervous system: Depression, aseptic meningitis, blurred vision, color vision disorders, decreased visual acuity due to drug poisoning
Blood: Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, eosinophilia, agranulocytosis, anemia
Liver: Gallbladder contractility, abnormal liver function tests, hepatotoxicity
Urogenital/genitourinary: Cystitis, hematuria, acute renal failure, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome
Immediately notify your doctor or pharmacist of any adverse reactions encountered while using the drug.
Drug Interactions:
Other Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): May increase risk of bleeding and ulceration.
Ibuprofen should be avoided in combination with aspirin unless taking a low dose of aspirin (<75 mg daily) to minimize risk.
Anticoagulants: NSAIDs can enhance the effect of warfarin, increasing bleeding risk.
Diuretics & Antihypertensive drugs: NSAIDs may reduce effectiveness of these drugs.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Antibiotics: May increase the effects of quinolones on the central nervous system.
Antacids: Enhances ibuprofen absorption, but aluminum hydroxide reduces absorption.
Methotrexate: Increases methotrexate toxicity.
Digoxin: NSAIDs increase plasma digoxin concentrations.
HIV Medication (Zidovudine): Increased risk of hematologic toxicity.
Tacrolimus: NSAIDs increase the risk of nephrotoxicity.
Mifepristone: NSAIDs should not be used 8-12 days after taking mifepristone as they may reduce effectiveness.
Due to a lack of compatibility studies, this drug should not be mixed with other drugs.
OVERDOSE:
Symptoms of ibuprofen overdose:
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, diarrhea, tinnitus, hearing loss, headache, drowsiness, dizziness.
Severe cases:
Central nervous system toxicity (seizures, loss of consciousness, respiratory depression).
Metabolic acidosis.
Prolonged bleeding time.
Treatment of Overdose:
Symptomatic treatment and gastric lavage if needed.
Activated charcoal is beneficial to limit ibuprofen absorption.
Correct metabolic acidosis and monitor renal function.
⚠ Severe poisoning is rare in children. Fatalities have not been reported at doses below 100 mg/kg.
Pharmacodynamics & Pharmacokinetics:
Mechanism of Action:
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, reducing pain, inflammation, and fever.
Ibuprofen reduces renal blood flow, which may cause fluid retention in patients with renal impairment, cardiovascular issues, or hypertension.
Absorption & Elimination:
Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Maximum plasma concentration is reached 1-2 hours after administration.
Plasma half-life: ~2 hours.
Eliminated via urine (12% unchanged, 14% conjugated).
Manufacturer Information:
HA TINH PHARMACEUTICAL JSC
Address: No.167 Ha Huy Tap Street, Nam Ha Ward, Ha Tinh City, Ha Tinh Province, Vietnam
Keep out of reach of children.
Consult the leaflet carefully before use.
Consult a doctor or pharmacist for more information.