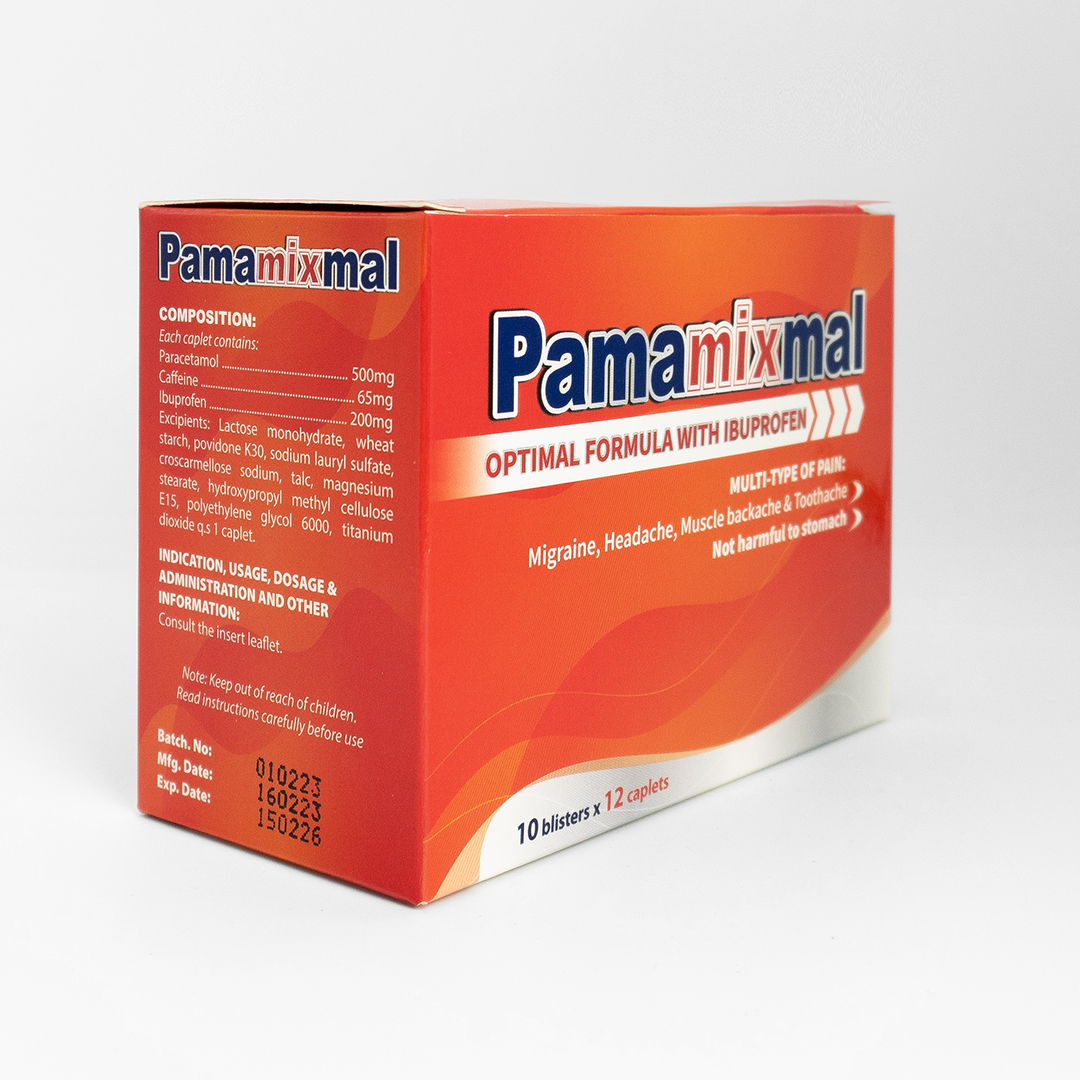
Dosage:
-Adults and children 16 years old and older: 2 caplets each 4-6 hours x 4 times daily. Do not exceed 8 caplets in 24 hours.
-Children from 12 to 15 years old: 1 caplet each 4-6 hours x 4 times daily. Do not exceed 4 caplets in 24 hours.
-Not recommended for children under 12 years old.
Usage: Taken oraly
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to paracetamol, caffeine or to any of the ingredients.
Warnings and important when using drugs
Ask doctor before using this medicine:
If you have liver disease or are careful, include alcoholic liver disease.
Paracetamol is not toxic at therapeutic doses, and when used under the guidance of a physician. However, overdose of paracetamol can cause liver failure. Taking multiple products containing paracetamol (aminophen) at the same time can lead to harmful consequences (such as paracetamol overdose).
Do not exceed the prescribed dose.
You should avoid drinking too much caffeine (e.g. coffee, tea and some cans) when using this product.
This medicinal product contains lactose. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, cases of lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
Using drugs for pregnant and lactating women
Pregnant:
The use of paracetamol-caffeine during pregnancy is not recommended due to the increased risk of weight gain and spontaneous
abortion associated with caffeine use
Breastfeeding women:
Caffeine in breast milk can have a stimulant effect on breastfed babies.
Due to the caffeine content of this product, it is not recommended for use if you are pregnant or breastfeeding
Effects of the drug on the ability to drive and use machines
The drug has no effect
Drug interactions and incompatibilities
The rate of absorption of paracetamol may be increased by metaclopramide domperidone and absorption decreased by colestyramine. The anticoagulant effect of warfarin and other coumarins can be enhanced by regular, prolonged daily use of paracetamol with an increased risk of bleeding; dosages are sometimes not significantly effective.
Since there are no incompatibility studies, this drug should not be mixed with other drugs.
Undesirable effects
For Paracetamol:
Uncommon, 1/1000 <ADR <1/100
Skin: rash
Digestion: Nausea, vomiting,
Hematology: Hematopoietic disorders (neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia), anemia.
Kidney: Kidney disease, kidney failure if tortured for a long time.
Rarely, ADR < 1/1000
Skin: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Lyell’s syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.
Other: Hypersensitivity reactions.
*For Caffeine:
Central nervous system: Nervous tension, dizziness.
When the recommended paracetamol-caffeine regimen is combined with dietary caffeine intake, caffeine intake may increase, possibly increasing caffeine-related side effects such as insomnia, restlessness, anxiety, difficulty pain, headaches, digestive disorders and palpitations.
*For Ibuprofen
Common:
Headaches
Felling dizzy
Felling sick (nausea)
Being sick (vomiting)
Wind
Indigestion
Call a doctor straight away if you have:
black poo or blood in your vomit – these can be signs of bleeding in your stomach
swollen ankles, blood in your pee or not peeing at all – these can be signs of a kidney problem severe chest or stomach pain – these can be signs of a hole in your stomach or gut
difficulty breathing, or asthma symptoms that become worse.
How to manage ADR: Stop taking the drug.
Inform your doctor or pharmacist immediately of any adverse reactions
Overdose and treatment
For Paracetamol:
* Symptom:
Paracetamol toxicity can be caused by a single toxic dose, by repeated large doses of paracetamol (eg, 7.5-10 g daily, for 1-2 days), or by long-term use. Dose-dependent hepatic necrosis is the most serious acute toxic effect of overdose and can be fatal.
Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain usually occur within 2 to 3 hours of taking a toxic dose. Methemoglobin blood, leading to cyanosis of the skin, mucous membranes and nails is a characteristic sign of acute poisoning with p-aminophenol derivatives; Small amounts of sulfhemoglobin may also be produced. Children tend to make methemoglobin more easily than adults after taking paracetamol.
In severe poisoning, there may be initial CNS stimulation, agitation and delirium. This may be followed by central nervous system depression; stupor, hypothermia; exhausted; rapid, shallow breathing: fast, weak, irregular pulse; low blood pressure; and circulatory failure. Vascular collapse due to relative hypoxia and because of the central inhibitory effect, this effect occurs only with very large doses. Shock can occur if multiple vasodilation. Fatal choking convulsions may occur. Usually coma occurs before sudden death or several days after coma.
Clinical signs of liver damage become apparent within 2 to 4 days after ingestion of a toxic dose. Plasma aminotransferases are elevated (sometimes very high) and plasma bilirubin levels may also be elevated: Furthermore, when the liver is severely damaged, the prothrom- bin time is prolonged. It is possible that 10% of patients with untreated poisoning have severe liver damage; of which 10% to 20% eventually die of liver failure. Acute renal failure also occurs in some patients. Liver biopsy showed central lobular necrosis with the exception of the periportal region. In non-fatal cases, liver damage can be reversible in weeks or months.
- To solve:
Early diagnosis is important in the treatment of paracetamol overdose. There are methods for the rapid determination of drug plasma concentrations. However, treatment should not be delayed pending test results if the history suggests a serious overdose. When intoxication is severe, it is important to provide active supportive treatment, Gastric lavage in all cases, preferably within 4 hours of ingestion.
The primary detoxification therapy is the administration of sulfhydryl compounds, which presumably work in part by replenishing the liver’s stores of glutathione.
N-acetylcysteine is effective when taken orally or intravenously. The medicine must be given immediately if it has not been 36 hours since paracetamol has been taken. Treatment with N-acetylcysteine is more effective when the drug is administered less than 10 hours after taking paracetamol. When giving orally, dilute the N-acetylcysteine solution with water or a non-alcoholic beverage to get a 5% solution and must be drunk within 1 hour after mixing. Give oral N-acetylcysteine with a first dose of 140 mg/kg, then give another 17 doses, each dose of 70 mg/kg every 4 hours. Discontinue treatment if plasma paracetamol test indicates a low risk of hepatotoxicity.
Adverse effects of N-acetylcysteine include skin rash (including urticaria, which does not require discontinuation), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and anaphylactic reactions.
If N-acetylcysteine is not available, methionine can be used. Alternatively, activated charcoal and/or salt bleach can be used, which may reduce paracetamol absorption.
For Caffeine:
* Symptom:
Caffeine overdose can lead to epigastric pain, vomiting, edema, tachycardia or arrhythmias, central nervous system stimulation (insomnia, restlessness, euphoria, agitation, tremor, tremor and convulsions).
It should be noted that for clinically significant caffeine overdose to occur with this product, the amount used will be related to the severe toxicity of paracetamol.
*To solve:
Patients should receive general supportive care (eg, hydration and maintenance of vital signs). The use of activated charcoal may be beneficial when taken within an hour of an overdose, but can be considered up to four hours after an overdose. The CNS effects of overdose can be treated with intravenous sedation.
Sodium Bicarbonate:
High doses of sodium bicarbonate can cause stomach symptoms including belching and nausea. In addition, high doses of sodium bicarbonate can cause hyperkalemia; Electrolytes should be applied and the patient monitored.
For Ibuprofen:
* Symptom:
Overdose symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, drowsiness, black or bloody stools, coughing up blood, shallow breathing, fainting, or coma.
*To solve:
Seek emergency medical attention.
Note: Keep out of reach of children. Read instructions carefully before use.
MANUFACTURED BY: HA TINH PHARMACEUTICAL JOINT STOCK COMPANY
No.167 Ha Huy Tap Street, Nam Ha Ward, Ha Tinh City, Ha Tinh Province, Vietnam.